
Caffeine is also an outlier as its use is seen as socially acceptable in most cultures and even encouraged in others.Ĭaffeine has both positive and negative health effects. Unlike most other psychoactive substances, caffeine remains largely unregulated and legal in nearly all parts of the world. Caffeine is the world's most widely consumed psychoactive drug. In 2020, almost 10 million tonnes of coffee beans were consumed globally. Caffeine-containing drinks, such as coffee, tea, and cola, are consumed globally in high volumes. To make these drinks, caffeine is extracted by steeping the plant product in water, a process called infusion. People may drink beverages containing caffeine to relieve or prevent drowsiness and to improve cognitive performance. The best-known source of caffeine is the coffee bean, the seed of the Coffea plant. It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America, and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as encouraging consumption by select animals such as honey bees. Ĭaffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A 1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. It is mainly used recreationally or as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance.
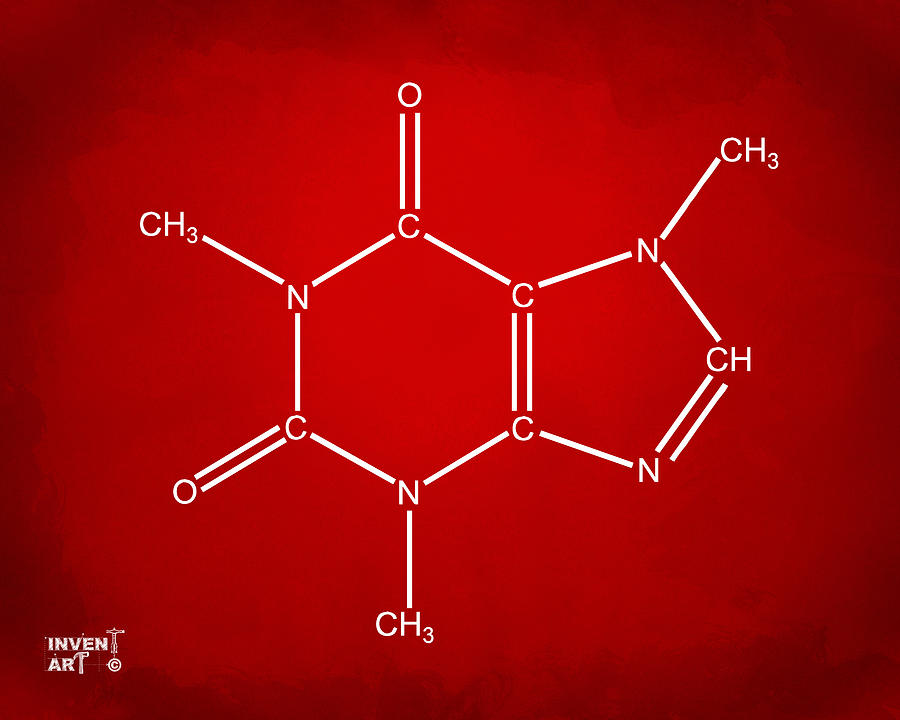

Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
